Security, responsibility and trust in Azure
AZ900
Shared responsibility of cloud security
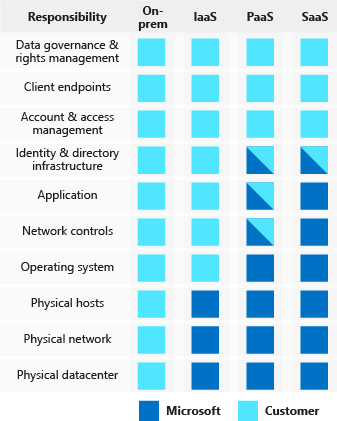
Regardless of the deployment type, you always retain responsibility for:
Data
Endpoints
Accounts
Access Management
Layered approach to security
Data
It is the responsibility of those storing and controlling access to the data to ensure that it’s properly secured. There are often regulatory requirements for the CIA of this data
Application
Ensure applications are secure and free of vulnerabilities
Store sensitive application secrets in a secure storage medium
Make security a design requirement for all application development
Compute
Secure access to virtual machines
Implement endpoint protection and keep systems patched and current
Networking
Limit communication between resources
Deny by default
Restrict inbound internet access and limit outbound, where appropriate
Implement secure connectivity to on-premises networks
Perimeter
Use DDoS protection
Use perimeter firewalls to identify and alert on malicious attacks against your network
Identity and access
Control access to infrastructure and change control
Use single sign-on and multi-factor authentication
Audit events and changes
Physical security
- Physical building security and controlling access to computing hardware within the data center is the first line of defence
Azure Security Center
Security Center can:
Provide security recommendations based on your configurations, resources and networks
Monitor security settings and automatically apply required security to new services
Continuously monitor services to provide automatic security assessments
Use machine learning to detect and block malware from being installed
Analyse and identify inbound attacks
Provide just-in-time access control for ports
Pricing Tiers
Free - Just assessments and recommendations of resources
Standard - Including continuous monitoring, threat detection etc.
Usage scenarios
You can use Security Center to:
Detect - Review the first indication of an event investigation
Assess - Perform the initial assessment to obtain more information about the suspicious activity
Implement a recommended security policy
Identity and access
Azure Active Directory
Azure AD provides services such as:
Authentication
Single Sign-On - One ID and password for multiple services
Application management
Business-to-Business identity services
Business-to-Customer identity services
Device management
Providing identities to services
Service Principals
Managed identities for Azure services
This makes creating service principles easier. A managed identity can be instantly created for any Azure service that supports it.
Role based access control
Roles are sets of permissions that users can be granted to access an Azure service instance.
Identities are mapped to roles directly or through group membership.
Roles can be granted at the individual service instance level, but they also flow down the Azure Resource Manager hierarchy.
Privileged Identity Management
This is an additional offering that provides oversight of role assignments to ensure people don’t have excess privileges.
Encryption
Encryption on Azure
Azure Storage Service Encryption - For data at rest
Azure Disk Encryption - Encrypt virtual machine disks
Transparent data encryption - Protect Azure SQL database and Azure data warehouse
Azure key vault - encrypt secrets
Benefits of using key vault:
Centralized application secrets
Securely stored secrets and keys
Monitor access and use
Simplified administration of application secrets
Integrate with other Azure services
Azure Certificates
Certificates in Azure are x.509 v3 and can be signed by a CA or self signed
Service Certificates
These are attached to cloud services and enable secure communication to and from this service.
These are managed separately from the services.
Management certificates
These allow you to authenticate with the classic deployment model
Protect your network
To provide inbound protection at the perimeter, you have several choices:
Azure Firewall - Managed cloud based network security service
Azure Application Gateway - Load balancer that includes a web application firewall
Network Virtual Appliances (NVAs) - Ideal for non-HTTP services or advanced configs
DDoS Protection
Basic:
Automatically enabled
Always on traffic monitoring and real time mitigation of common network level attcks
Standard:
Can mitigate:
Volumetric attacks - Flooding network layer with traffic
Protocol attacks - Exploit weakness in layer 3 and layer 4 protocol stack
Resource layer attacks - Target web application packets to disrupt the transmission of data between hosts
Virtual network security
For communication between virtual machines, Network Security Groups are a critical piece to restrict unnecessary communication.
This allows you to filter network traffic to and from Azure resources in an Azure virtual network
Network Integration
To provide a dedicated private network between your network and Azure, you can use Azure ExpressRoute.
Protecting shared documents
Azure information protection - A cloud-based solution to help organizations classify and optionally protect documents by applying labels
Azure Advanced Threat Protection
This is a cloud-based solution to identify, detect and help to investigate threats.
It has the following components:
ATP portal - Allows you to monitor and respond to suspicious activity
ATP sensor - Installed directly on domain controllers to monitor traffic
ATP cloud service - Runs on Azure infrastructure and is connected to Microsoft’s intelligent security graph
Security considerations for Application Lifecycle Management Solutions
Provide training to ensure everyone knows the threats
Define security requirements - Update continuously to address change in threat landscape.
Define metrics and compliance reporting - Have minimum levels of security quality
Perform threat modelling - Allows development teams to consider the security implications of designs
Establish design requirements - Specific security features must be implemented
Define and use cryptography standards
Manage security risks from using third-party components - Keep an accurate inventory and plan to respond when new vulnerabilities are discovered
Use approved tools - Define and publish a list of approved tools
Perform Static Analysis Security Testing - Analyse source code prior to compilation
Perform Dynamic Analysis Security Testing - Analyse fully-compiled code
Perform penetration testing
Establish a standard incident response process