Principles of cloud computing
AZ900
What is cloud computing
Services typically offered
Compute power
Storage
Networking
Analytics
Containers - Provide a consistent, isolated execution environment for applications.
Standard runtime environment used to execute the app
Leading platform is docker
Serverless computing - Run application code without creating, configuring or maintaining a server
Application is broken into separate functions that run when triggered by some action
Only pay for the processing time used by each function as it executes
Benefits of cloud computing
Cost effective
No upfront infrastructure costs
Not buying infrastructure that isn’t fully utilised
Can scale up and down with demand
Scalability
Vertical scaling (scaling up)
- Adding more resources to a server
Horizontal scaling (scaling out)
- Adding more servers
Elasticity
- Automatically adding more resources to handle traffic
Current
- Don’t have to think about having current hardware and patches
Reliability (Microsoft responsibility)
Provided backup, recovery replication etc
Fault tolerance
Global
Fully redundant datacenters
High availability (shared responsibility)
Lower customer latency
Security (shared responsibility)
- Both physical and digital
Agility (speed to set up)
Compliance terms and requirements
Questions include:
How compliant is the cloud provider when it comes to handling sensitive data?
How compliant are the services offered by the cloud provider?
How can I deploy my own cloud-based solutions to scenarios that have accreditation or compliance requirements?
What terms are part of the privacy statement for the provider?
Economies of scale
Less expensive
More efficient
Pass benefits on
CapEx vs OpEx
CapEx (Capital expenditure)
Spend on physical infrastructure
Storage
Network
Backup and archive
Organisation continuity and disaster recovery
Datacentre infrastructure
Technical personnel
Benefits
Fixed costs make prediction easier
OpEx (operational expenditure)
Monthly bill
Pay as you go
Get set up immediately
No upfront costs
Leasing software and customised features
Scaling charges based on usage/demand
Billing at the user or organisation level
Azure follows a consumption based model, which just has operational expenditure
Benefits
Easier to respond to change
Types of cloud models
| Name | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Private Cloud | Cloud set up in own datacenter |
|
|
| Public cloud | No local hardware, all running on cloud provider’s hardware |
|
|
| Hybrid Cloud | Combining public and private clouds |
| Increased cost and complexity |
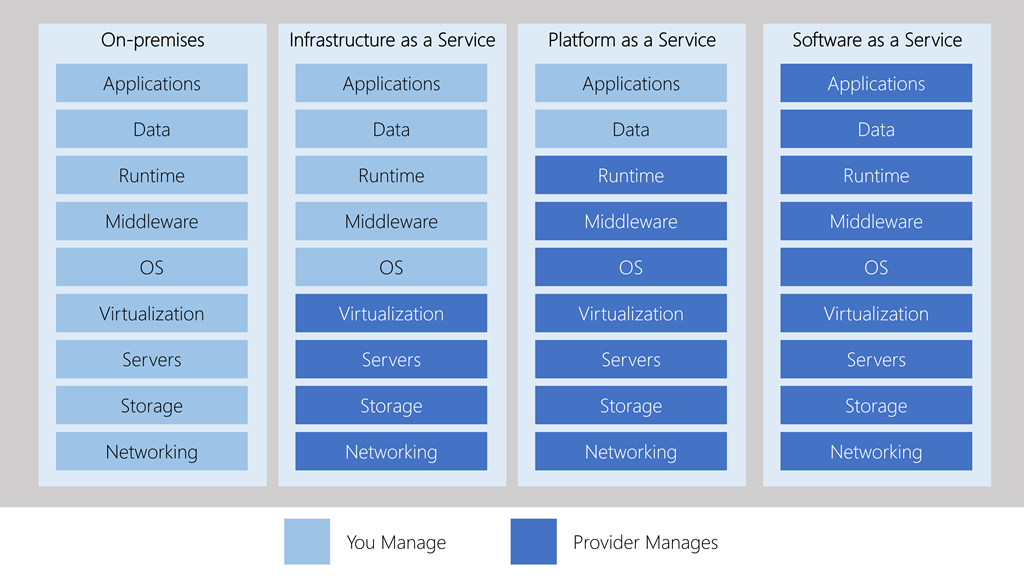
Types of cloud services
IaaS
Most flexible category; gives control over hardware.
Commonly used for:
Migrating workflows
Test and development
Storage, backup and recovery
Shared responsibility model - Cloud provider ensures infrastructure is working correctly, customer makes sure the service they are using is configured correctly, is up to date and is available to users.
PaaS
Provides an environment for building, testing and deploying software applications. Don’t have to manage infrastructure. Commonly used for:
Development framework
Analytics or business intelligence
SaaS
Only responsible for data+access
Access in Azure via marketplace
Pay-as-you-go pricing
Users pay for software they use on a subscription model
Cost and Ownership
| IaaS | PaaS | SaaS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upfront costs | None, pay for consumption | None, pay for consumption | None, pay subscription |
| User ownership | User responsible for software, OS, middleware and applications | User responsible for development of applications | Users just use software |
| Cloud provider ownership | Infrastructure is available to user | OS, Network and service | Provision, management and maintenance of application software. |