Introduction to Probability
DADS
Axioms of Probability
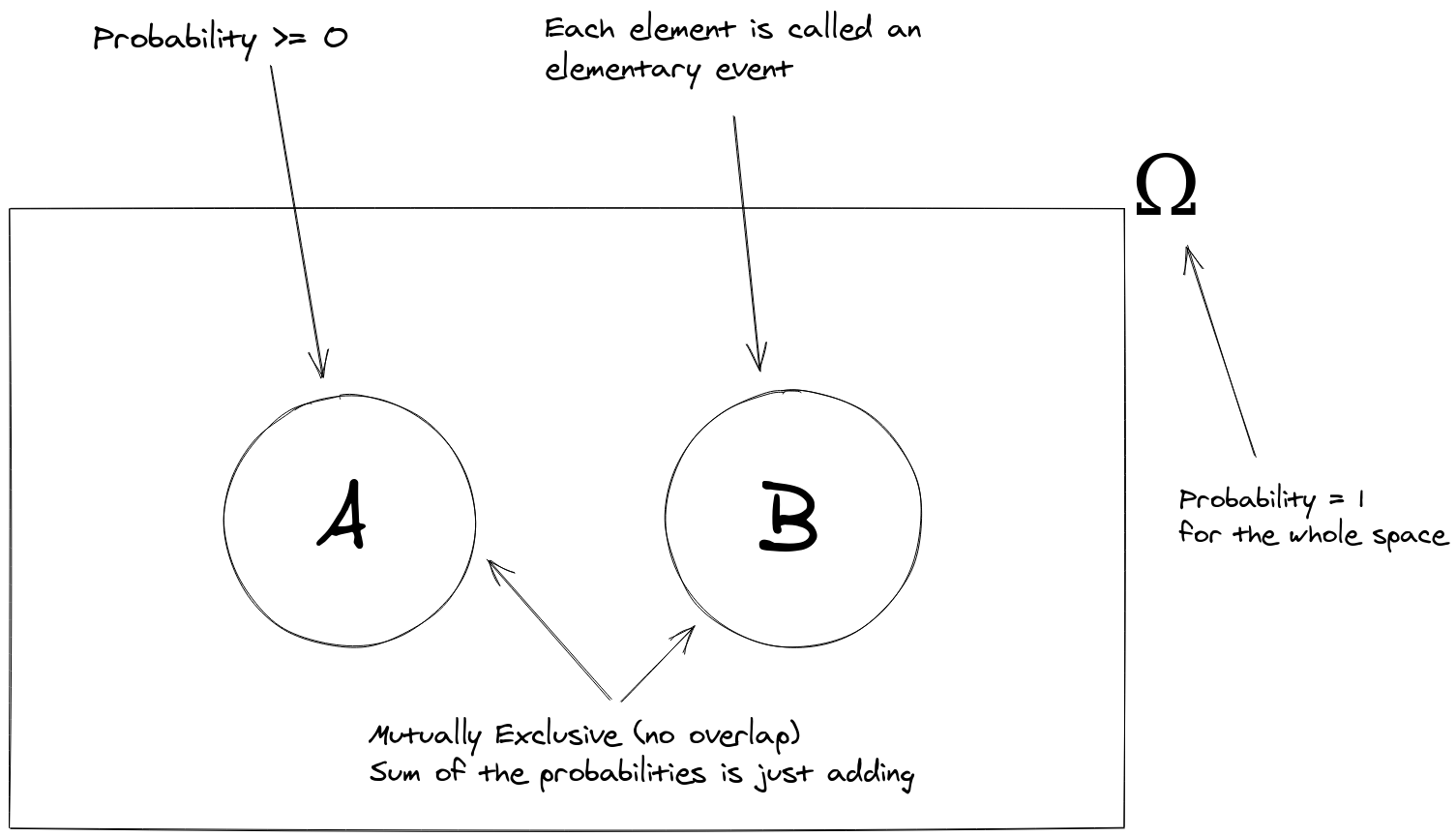
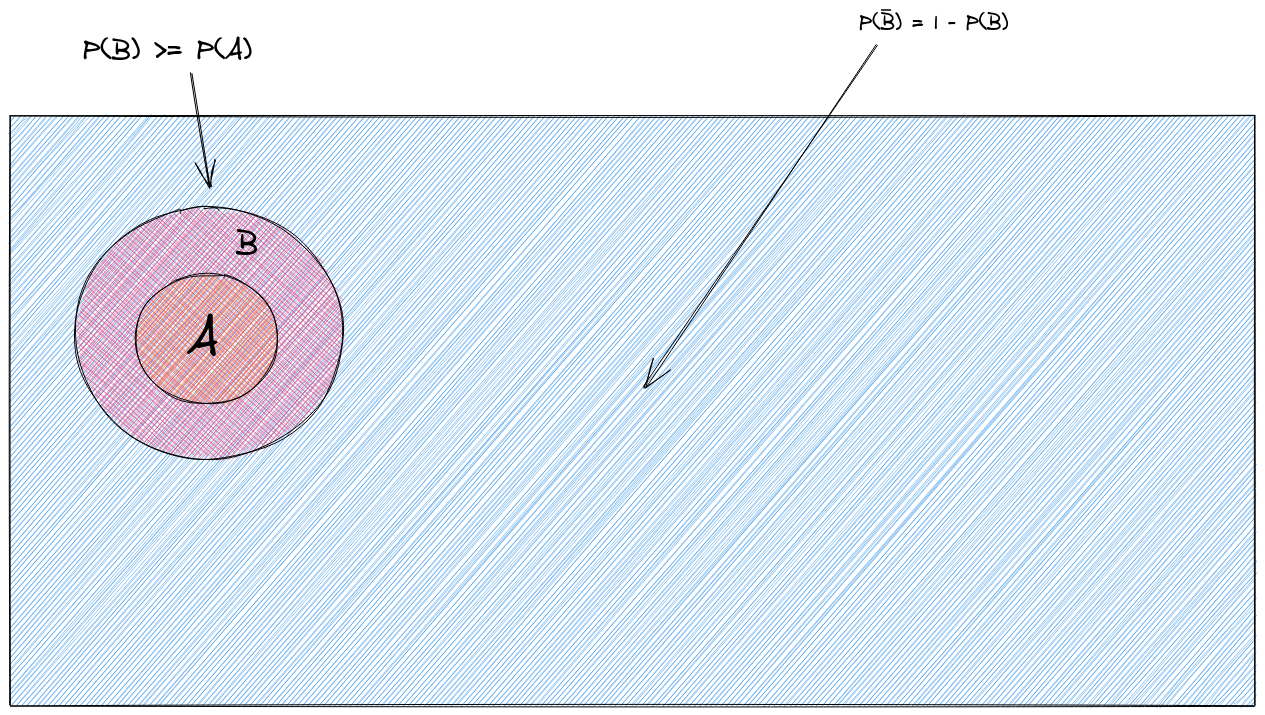
This then leads to further rules
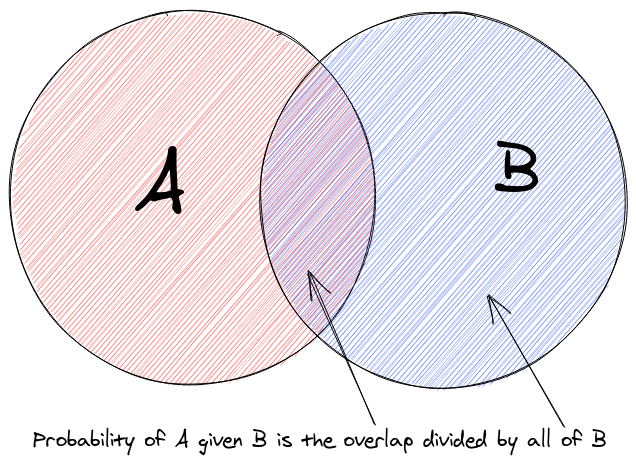
Conditional Probability
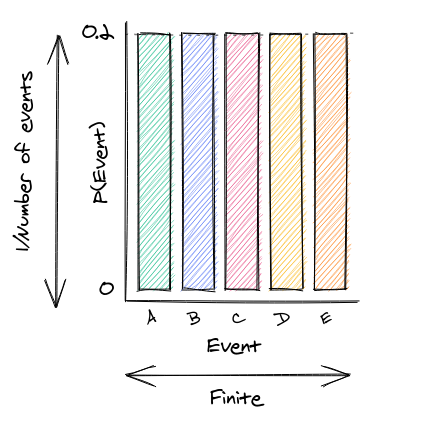
Uniform Distribution
Independent Probabilities
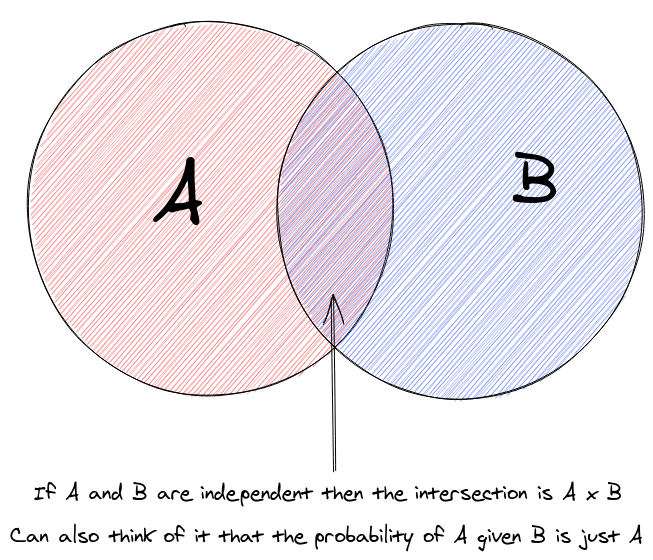
Pairwise Independence
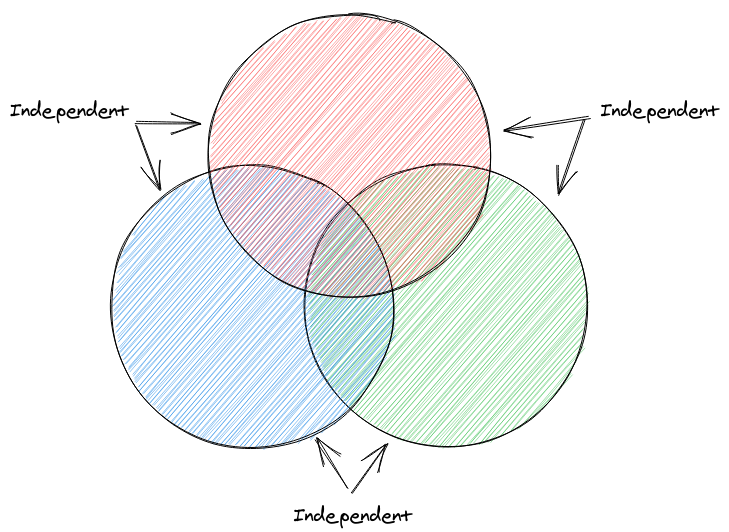
Every pair of events are independent of each other
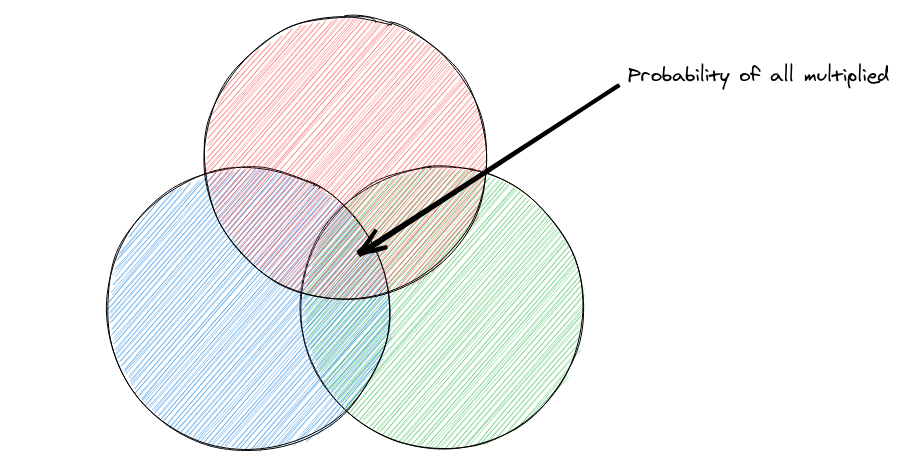
Mutual Independence
The probability of all of a subset of events happening in the multiplication
Random variable
The probability that a variable takes a certain value
Independence
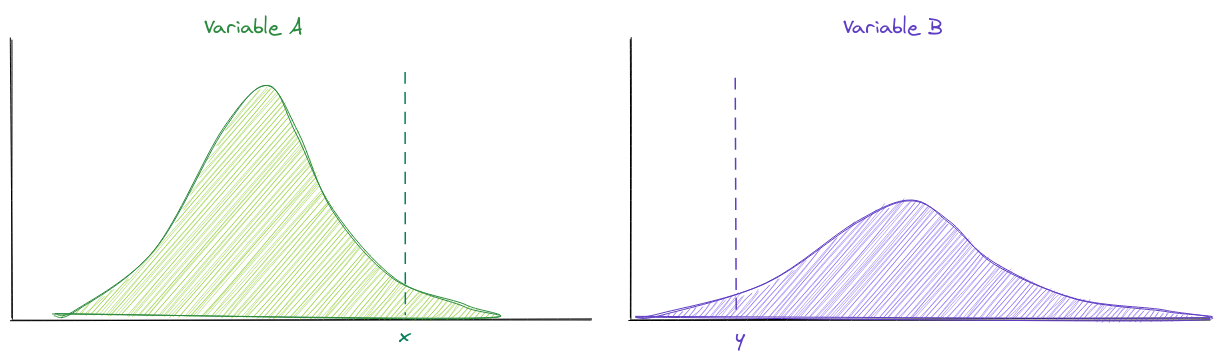
The probability $A=x$ and $B=y$ is the probability $A=x$ multiplied by the probability $B=y$
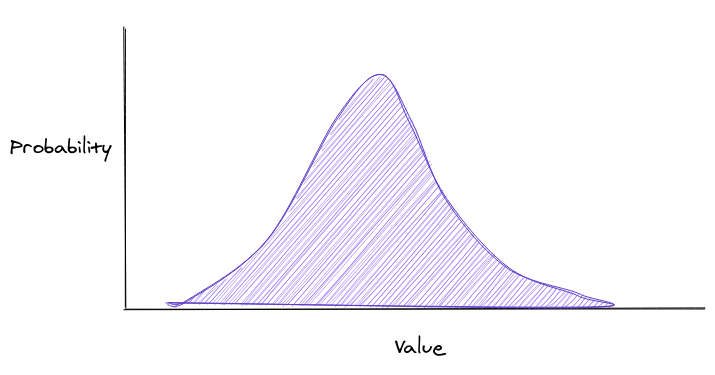
Expected value
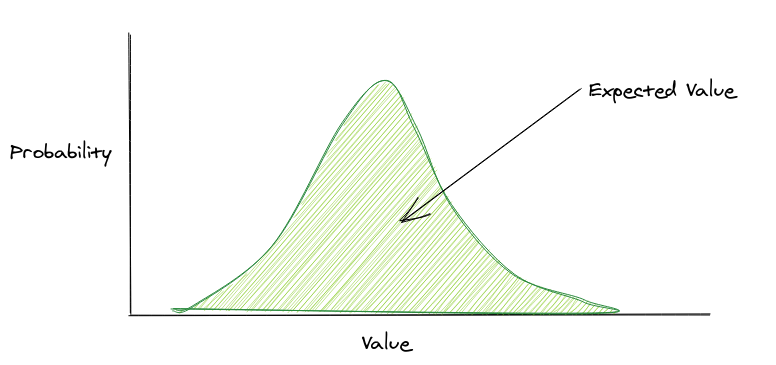
The expected value is x times the probability of x for all x
This can also be shown as the area under the curve
Linearity of expectation
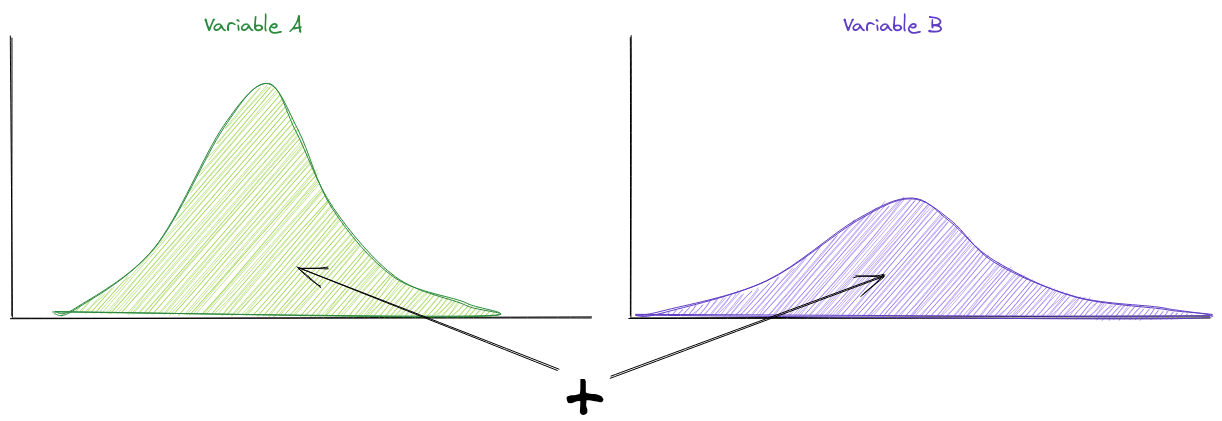
The expected value of A and B is the expected value of A plus the expected value of B
This doesn’t apply for multiplication, only if they are independent